For example, a company may choose this method to depreciate assets such as computers, which may become obsolete very quickly given the rate of technological advancements in the world today. The sum of years method uses the expected life and adds the digits for every year to give the final depreciation expense amount. Unit of production method calculates depreciation when the asset starts producing units and the cycle ends when the asset stops producing. This method is based on the units produced by assets rather than the time for which the asset is used. The method takes the total depreciation over the useful life of the asset and allocates this to each year in proportion to the remaining life of the asset at the beginning of the year.
Straight Line Depreciation Method
Consider a company that purchases a piece of machinery for $10,000 with a salvage value of $1,000 and a useful life of 5 years. The next step is to calculate the total depreciation required over the lifetime of the asset, which is simply the cost of the asset less its salvage value. In the second accounting period ending on 31 December 2021, 9 months out of the first year of the asset overlaps as well as 3 months out of the asset’s second year. Therefore, the depreciation expense for the second accounting period is equal to 9/12 ✕ $4000 plus 3/12 ✕ $3000. For example, in the first accounting period that ends on 31 December 2020, only 3 months out of the first year of the asset overlaps.
Calculate sum of the years’ digits depreciation
Computer equipment or vehicles are all good candidates for accelerated methods of depreciation like sum of years. Calculate depreciation over the useful life of the asset using the sum of the years’ digits method. Use this calculator to calculate an accelerated depreciation using the sum of years digits method. Businesses must account for depreciation and there are a few ways to do it, some better suited publication 504 divorced or separated individuals than others depending on the specific asset. The sum-of-the-years’ digits (SYD) is an accelerated method better suited for assets that depreciate more early in their useful life since accelerated depreciation assumes higher depreciation costs in the early years. The benefit of using an asset will decline as the asset gets older, meaning an asset provides greater service value in earlier years.
Advantages of the SYD Method
Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. It starts with the value n in the first year and decreases by 1 each year until it equals 1 in the final year of the asset’s estimated service life. High-tech products are examples of assets in which the decline of benefits is likely to follow such a pattern. As such, most of the cost of these assets should be allocated to these same early years.
It records a larger depreciation in the earlier years of the asset’s useful life. Straight-line depreciation recognizes the same amount of depreciation each period over the useful life of the asset. On the other hand, accelerated depreciation methods recognize a larger percentage of the total depreciation in earlier periods. This has the tax advantage of allowing a larger depreciation deduction faster. The sum-of-the-years’-digits depreciation (SYD depreciation) is one method for calculating accelerated depreciation. However, the total amount of depreciation over an asset’s useful life should be the same regardless of which depreciation method is used.
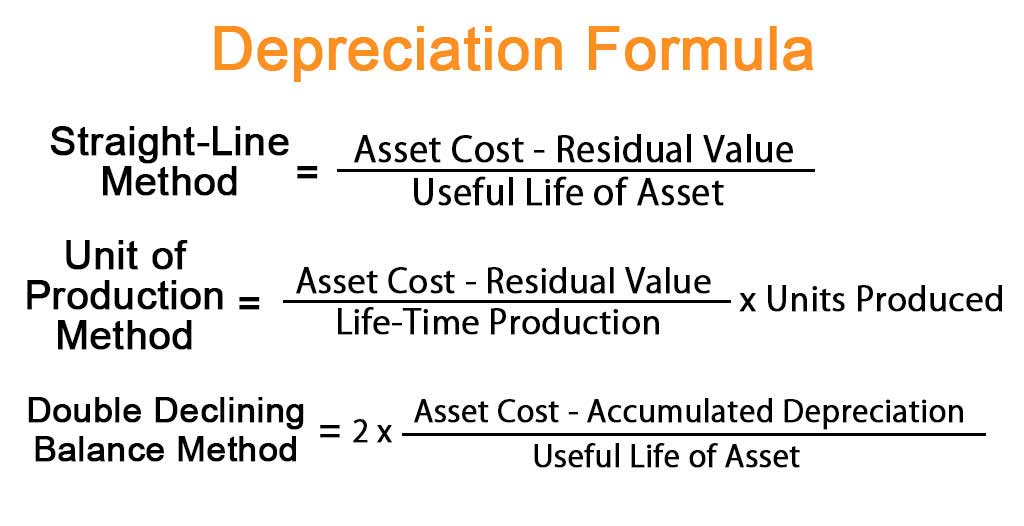
The straight-line method carries out the cost of the asset minus the salvage value, which is then divided by the useful life of the asset. Depreciation is carried out for tangible assets which are the physical assets. A company acquires these assets to increase productivity and raise the overall performance of the business. Intangible assets are amortized which is a concept similar to depreciation but the type of assets differ in both cases.
- In the third year, the asset value subject to depreciation would be expensed 3/15 (20%).
- Depreciation expenses are recorded for accounting purposes and its calculation is, therefore, important to a business.
- As such, with the accelerated methods of depreciation, companies account for higher depreciation expenses in the beginning and less maintenance costs.
- The sum of years depreciation method works by depreciating the asset’s depreciable amount by a depreciation factor unique to each year.
- The depreciation expense is higher at the beginning and lower towards the end to reflect that most of the value has been used at the start.
In this case, the company should use the sum of years digits depreciation method on the fixed assets that can produce higher productivity in the early year and such productivity will gradually drop down as time passes. This is a method that allocates higher depreciation expense in the initial years of asset use. Companies typically use accelerated depreciation to minimize their taxable income because it allows for greater depreciation expense deductions in the earlier years of the equipment or asset’s life. Accelerated depreciation methods could also be seen as more accurate, as they assume that an asset loses a majority of its value in the first few years of its use. We only need to calculate this value one time in an asset’s life when we estimate its depreciation for the first time. We will use the same value to calculate the depreciation expense of the future accounting periods.
11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. For example, suppose that a company purchases equipment on 1 October of the current year. The exception is that the calculations needed in sum-of-the-years’ digits are slightly more complex. CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path.
Once this is calculated, the depreciation expense can be estimated for all future years, which helps in budgeting and income projection for business owners. Sum of years is an accelerated depreciation method suitable for assets that lose most of their value in the early years of service. The depreciation expense is higher at the beginning and lower towards the end to reflect that most of the value has been used at the start.